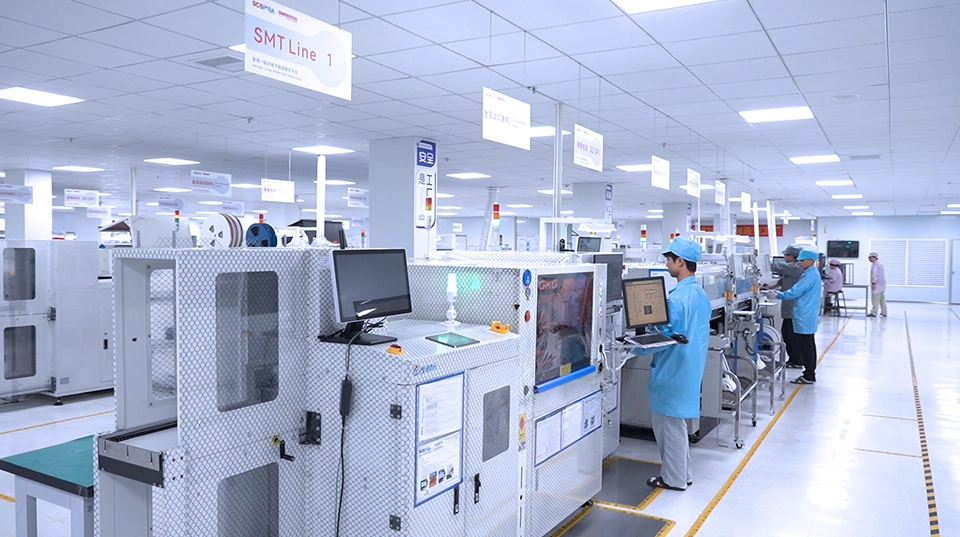
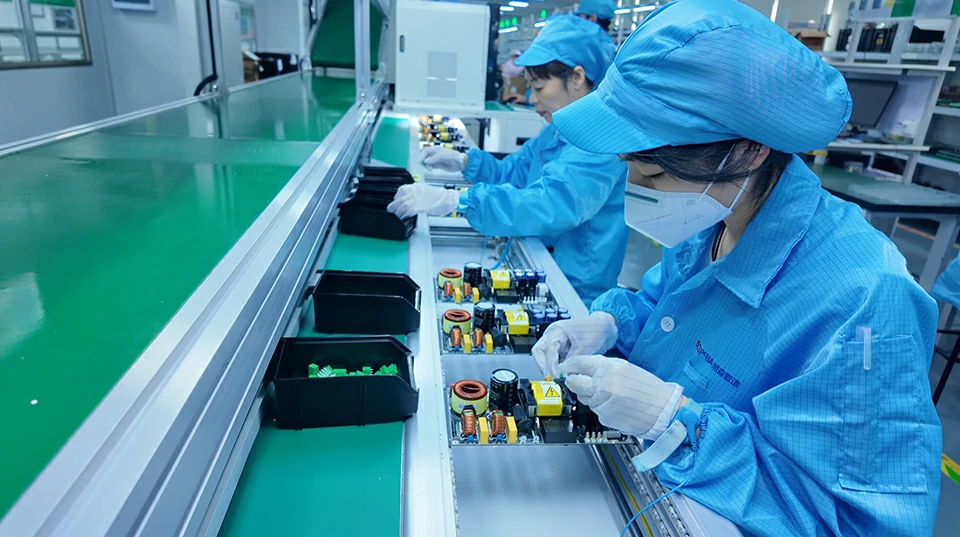
Contact Us
SUCCESS CIRCUITS GROUP LIMITED
Company established 2013 | Manufacturing sites: Shenzhen, Jiangsu, Jiangxi (China); Vietnam | Service centers: Wuhan (China), USA | All statistics are current as of 2026.
Tel: +86 (0)755-2561-8511
Email: [email protected]
US Add: 1363 Lincoln Ave, Suite 1, Holbrook, NY
China Add: Room 203, Building B, No. 229, Wanfeng Middle Road, Wanfeng Community, Xinqiao Street, Bao’an District, Shenzhen
Wuhan Add: Room 602, Ward Center, No.780 Gaoxin Avenue, East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan, China